[ad_1]
What would it be like to keep a piece of outer place in your hand? Some fortunate experts will uncover out soon when NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft (shorthand for Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer) returns from its seven-yr mission. The probe will fall off a canister keeping about a cup of pebbles and dust from the surface of the around-Earth asteroid Bennu. “Bennu is a time capsule of the early solar method, and we are cracking it open,” claims Amy Hofmann, an isotope geochemist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, who is a co-investigator on the mission. “We get to be the initial people to see what is in there. I’m getting goose bumps speaking about this.”
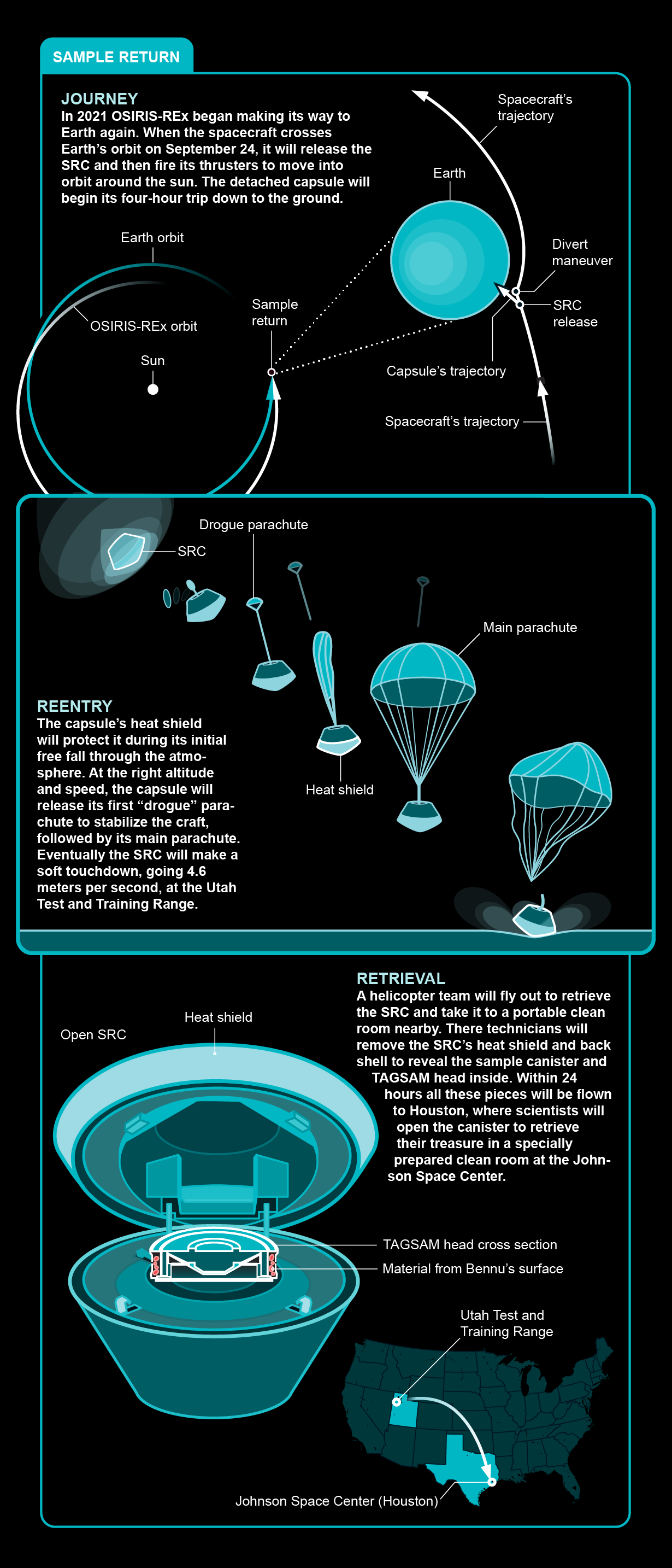
Hofmann is just one of close to 200 researchers who will obtain parts of the cargo OSIRIS-REx brings back again. On September 24 the probe is established to launch its sample return capsule, which will barrel as a result of Earth’s ambiance and make a parachute landing at the Office of Defense’s Utah Examination and Coaching Assortment. If all goes nicely, recovery groups will helicopter it to a moveable cleanse place to get rid of its heat defend and back again shell and then fly it to a specifically organized facility at the Johnson Space Center in Houston. Researchers there will diligently open the internal container, dealing with it within a glove box to retain out all contaminants, to retrieve some of the only pristine primordial bits of asteroid ever to access Earth’s area. (Meteorites are excellent, way too, but their unprotected burn off by our atmosphere alters them.)
The samples will expose the state of the solar technique when it was initial forming, including which amino acids and other chemical compounds essential for biology have been present. “The ‘O’ in ‘OSIRIS-REx’ is really for the origin of everyday living,” states Dante S. Lauretta of the University of Arizona, the mission’s principal investigator. “We want to understand the position that these carbon-loaded asteroids played in providing the precursors of everyday living to Earth.”
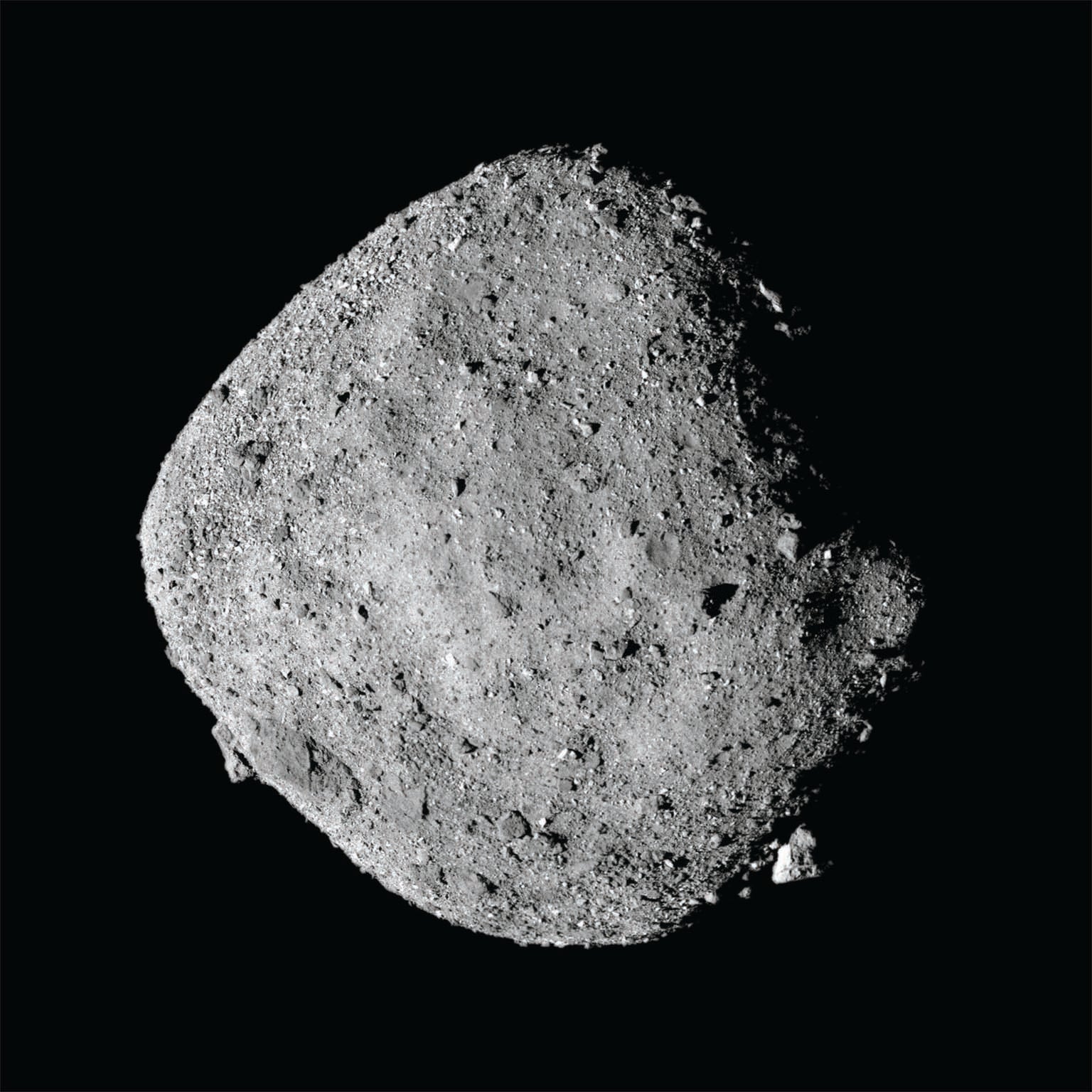
OSIRIS-REx launched in 2016 and arrived at Bennu in 2018. It spent two several years close to the space rock, building measurements with its onboard cameras, spectrometers, and other instruments. People scans discovered a whole lot about Bennu, such as that it truly is a lot more like a pile of loosely certain rubble than a sound object and that it holds drinking water-bearing minerals. But the real payoff will be the samples. “We have obtain to the absolute state-of-the-art know-how here on Earth,” states co-investigator Michelle Thompson, a planetary scientist at Purdue College. “Having time, getting this large workforce and the means to do coordinated analyses, to look at the very same sample with various unique techniques—there’s really practically nothing that can replace that. Sample return is a cornerstone of planetary science.”
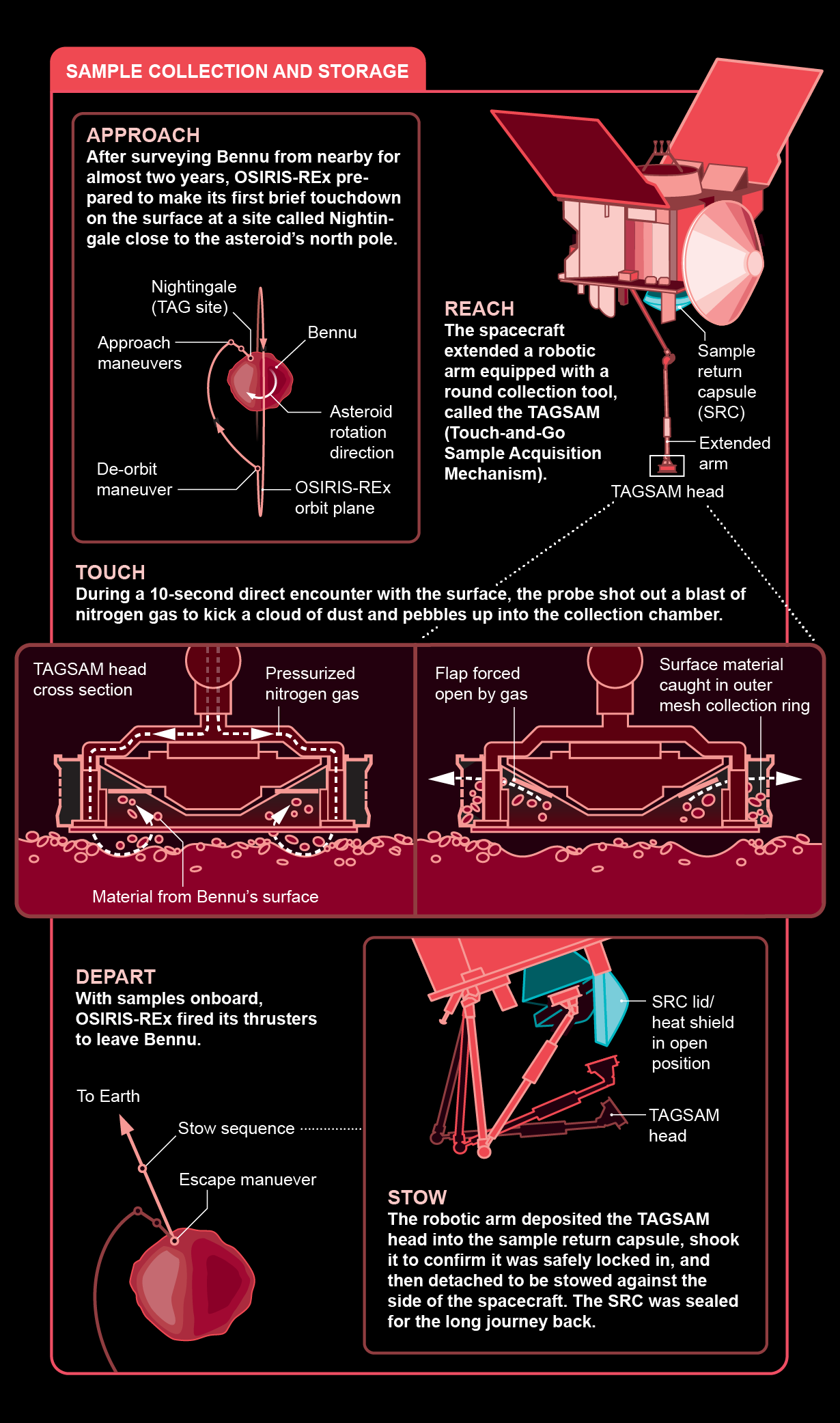
In October 2020 the spacecraft created a near solution to the asteroid, briefly touching the floor with its Touch-and-Go Sample Acquisition System (TAGSAM), a robotic arm that fired a burst of nitrogen fuel to stir up dust and rock, which it then funneled into its collector head. “It appears like an air filter, except we brought the air,” Lauretta states. Images taken in the course of the selection course of action recommend the mission scooped up lots of material. Some additional bits of sample even bought trapped to the outdoors of the TAGSAM.
 

Soon after scientists open up the TAGSAM again on Earth, a quarter of its haul will go to the OSIRIS-REx team, who will disperse it from the Johnson Place Center to laboratories around the environment. 4 percent of the sample will go to Canada, a contributor to the mission, and at least .5 % will be despatched to Japan, which carried out the two Hayabusa missions that brought again the world’s 1st asteroid samples in 2010 and 2020. But 70 per cent of the things returned will continue being untouched by anyone, at minimum for now. “Just like with Apollo, we want to maintain the extensive vast majority of the samples for potential experts,” claims College of Arizona planetary scientist Andrew Ryan, chief of the OSIRIS-REx Sample Bodily and Thermal Investigation Performing Group. “We’ll have new questions, there will be long term instruments, and we want to make sure we haven’t burned through the entire sample.”
Even the initially scientific results must drastically develop our understanding of asteroids like Bennu. Ryan’s workforce will evaluate how considerably warmth the materials conducts, how a lot room there is between particles in each grain, and how robust the power is that holds the items collectively. Comparing their results with estimates scientists created when the spacecraft was orbiting Bennu will aid them superior characterize other asteroids from distant measurements—a perhaps essential capability if we want to deflect an Earth-certain rock in the potential.
Hofmann will use a exclusive form of mass spectrometer known as an Orbitrap to establish unique organic molecules with unique isotopic compositions in her samples and look at their amounts. Measuring the extent to which many carbon 13 atoms (a uncommon, secure type of carbon with an additional neutron) swap carbon 12 (the most widespread kind of carbon) in a particular molecule, for occasion, can tell researchers about the temperature when the compound fashioned. “These measurements were not even doable when OSIRIS-REx was 1st proposed,” Hofmann states. “It’s forensics for planetary science.”
Thompson will use electron microscopes to study how Bennu has been weathered above time by impacts from other place rocks and by energetic particles streaming off the solar. These measurements, put together with the results of other experiments planned for the samples, aim to give a in depth photo of the condition of our early solar process and how it grew to become what it is currently. “The inquiries we’re likely to respond to are very varied,” she claims. “[They cover] anything from being familiar with and characterizing the creating blocks of the photo voltaic method to wanting at the physical traits of the product. We are going to come out of this mission with a fully revolutionized comprehension of these kinds of bodies. Every person should be very psyched.”
.png)







[ad_2]
Resource url






