[ad_1]
January 1, 2024
3 min go through
The more substantial a mobile form is, the rarer it is in the body—and vice versa—a new study displays

Ni-ka Ford and Jen Christiansen
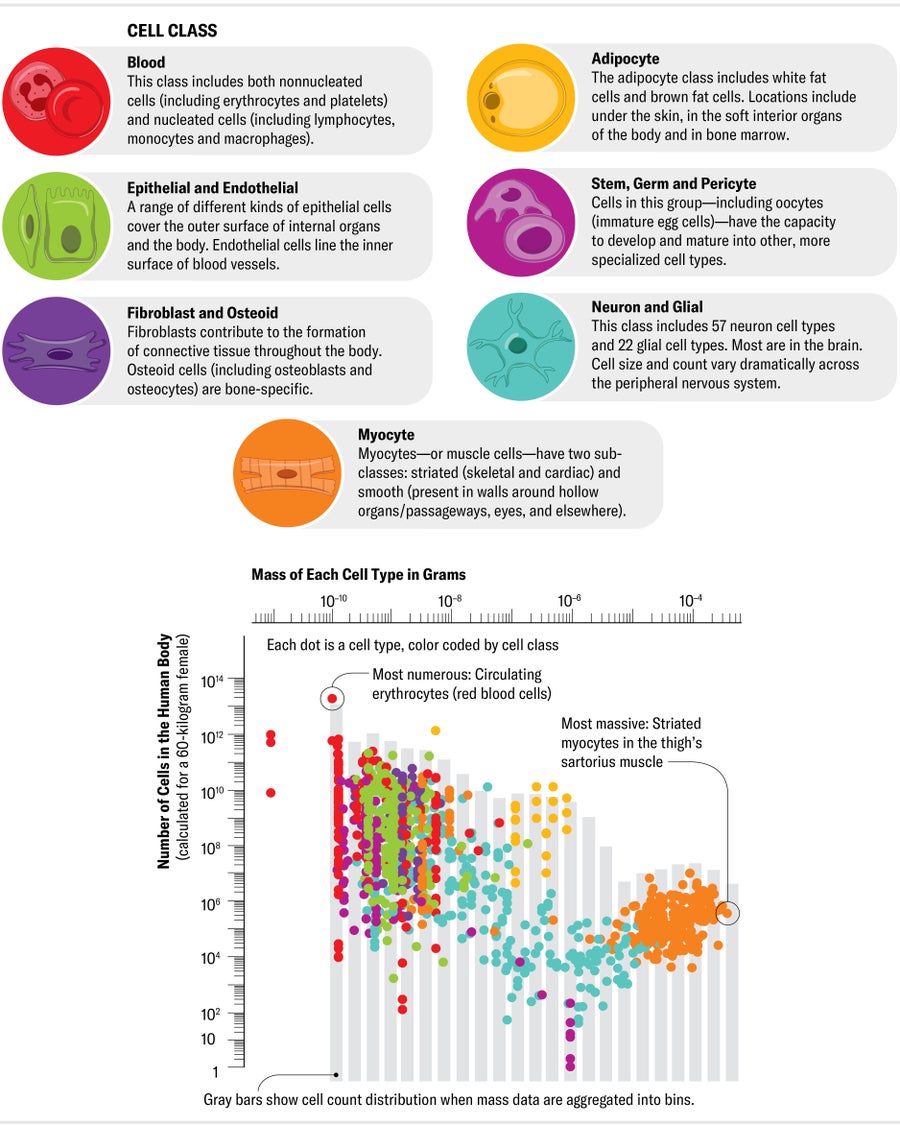
Many aspects of our environment, from the human body mass of creatures in the animal kingdom to the inhabitants of metropolitan areas throughout the world, observe an intriguing mathematical pattern. Known as Zipf’s legislation, the rule says that when something’s size is doubled, that factor results in being about half as widespread. Scientists puzzled no matter if the legislation prolonged to the human physique. Ecologist Ian A. Hatton of McGill University, unbiased researcher Jeffery A. Shander and their colleagues amassed knowledge about the quantity and frequency of human cells and seemed for the pattern. It turns out that it retains.
“As you double the volume of a mobile, the frequency of cells of that measurement is halved,” Hatton states. Teensy, nonnucleated pink blood cells are by much the most typical cells in our bodies, while the comparatively gigantic muscle cells in our arms and legs are the scarcest. Currently being equipped to use a cell’s measurement to estimate its frequency in the physique could assistance medical practitioners much better comprehend particular entire body devices and challenging-to-rely mobile styles, the scientists say. The examine implies, for instance, that immune cells termed lymphocytes are much far more widespread than biologists recognized.
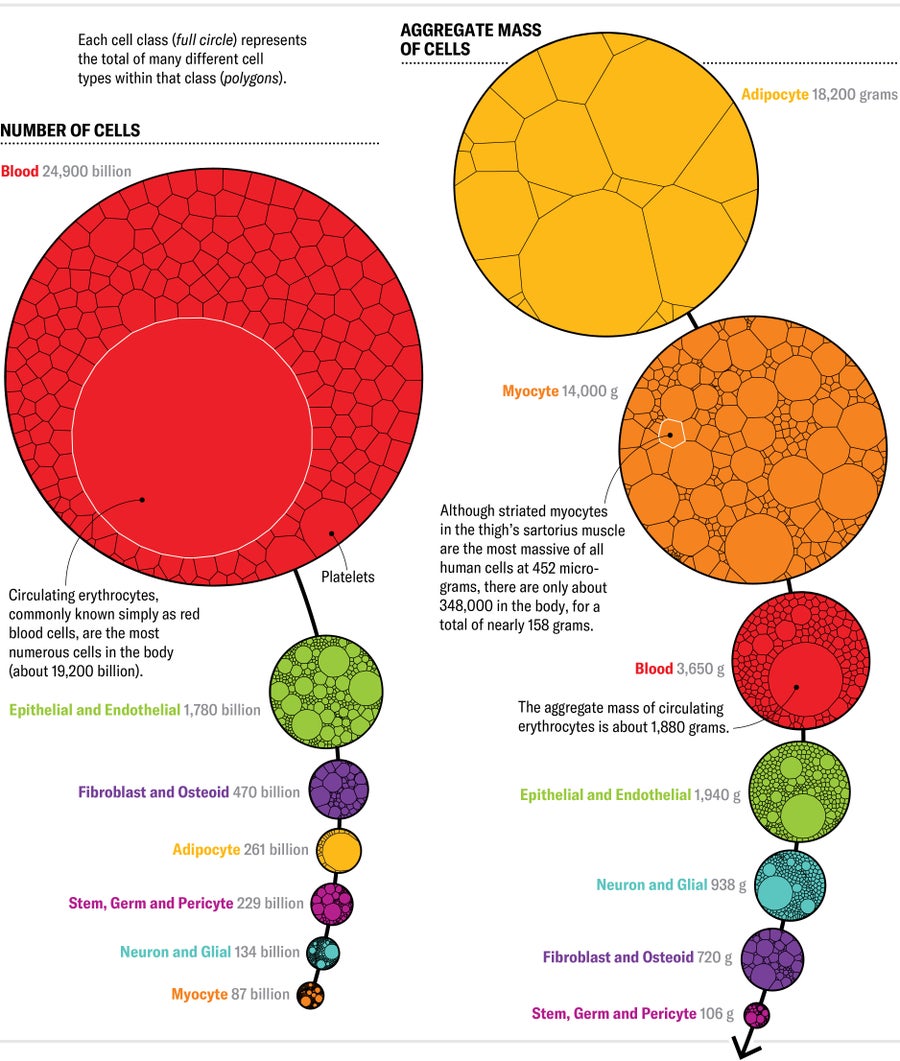
Quantity AND Combination MASS OF CELLS IN THE HUMAN Body, BY Mobile Class
(Calculated for a 60-kilogram female kind.) These two strands show the hierarchy of cells by amount (frequency in the human body) as very well as by how significantly complete biomass they account for in the body. The discrepancy in between the two occurs from the fact that the most numerous cells are often incredibly compact and consequently add only a modest sum of biomass, whilst the far more huge cells, nevertheless relatively unheard of, make up considerably of our heft. Whole mobile mass does not equivalent whole human body mass, because bodies also consist of huge volumes of drinking water.
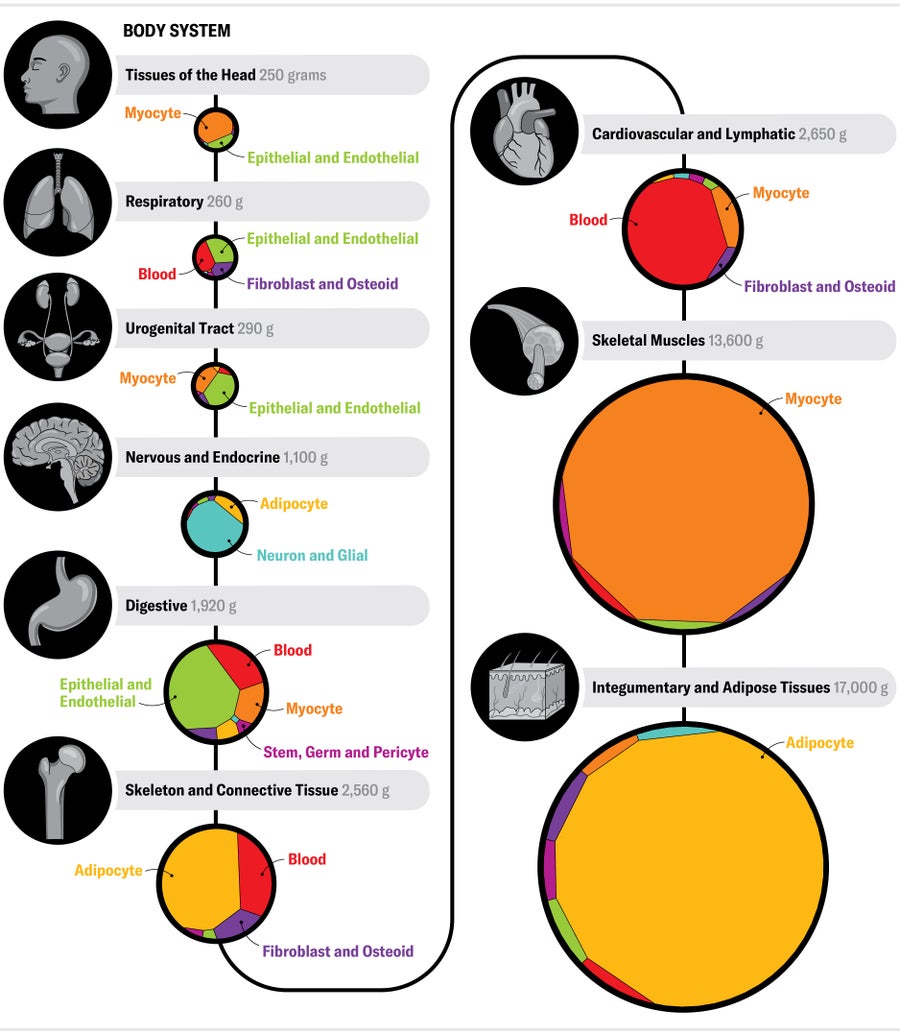
MASS OF Human body Programs
(Calculated for a 60-kilogram feminine variety.) Diverse units in the human physique account for differing quantities of our overall biomass. The largest process, the integumentary and adipose tissues, consists primarily of pores and skin and fats.
[ad_2]
Supply website link