[ad_1]
Artificial intelligence can structure an autonomous robotic in 30 seconds flat on a laptop computer or smartphone.
It is not quite time to panic about just anybody becoming able to create the Terminator while ready at the bus stop: as reported in a current analyze, the robots are easy devices that scoot along in straight lines devoid of accomplishing much more advanced tasks. (Intriguingly, having said that, they often appear to establish legs rather than an arrangement that will involve wiggling, going like an inch worm or slithering.) But with much more work, the method could democratize robotic layout, suggests examine author Sam Kriegman, a pc scientist and engineer at Northwestern College.
“When only significant providers, governments and large academic establishments have enough computational electrical power [to design with artificial intelligence], it genuinely limitations the range of the concerns getting requested,” Kriegman suggests. “Increasing the accessibility of these applications is a thing which is definitely remarkable.”
AI can now publish essays and push cars and trucks, so design may seem like a rational up coming phase. But it’s not effortless to generate an algorithm that can effectively engineer a real-world solution, claims Hod Lipson, a roboticist at Columbia College, who was not involved in the investigation. “Many thoughts keep on being,” Lipson says of the new research, “but I assume it is a large step forward.”
The technique utilizes a model of simulated evolution to make robots that can do a specific task—in this scenario, ahead locomotion. Earlier, producing evolved robots involved making random variations, testing them, refining the very best performers with new variants and tests these variations again. That involves a large amount of computing electricity, Kriegman says.
He and his colleagues rather turned to a technique identified as gradient descent, which is much more like directed evolution. The method begins with a randomly produced human body structure for the robotic, but it differs from random evolution by providing the algorithm the potential to gauge how perfectly a given system system will accomplish, as opposed with the suitable. For each and every iteration, the AI can house in on the pathways most very likely to direct to accomplishment. “We delivered the [algorithm] a way to see if a mutation would be fantastic or bad,” Kriegman suggests.
In their personal computer simulations, the researchers started off their robots as random shapes, gave the AI the concentrate on of creating terrestrial locomotion and then established the nascent bots loose in a digital atmosphere to evolve. It took just 10 simulations and a matter of seconds to reach an optimal state. From the unique, nonmoving physique approach, the robots were being in a position to start going at up to .5 system duration for every second, about 50 percent of the ordinary human walking pace, the researchers documented on October 3 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Usa. The robots also regularly evolved legs and started going for walks, the staff observed. It was spectacular that with just a couple iterations, the AI could build a little something purposeful from a random kind, Lipson says.
To see if the simulations worked in practice, the researchers created illustrations of their very best-performing robot by 3-D printing a mould of the style and design and filling it with silicone. They pumped air into smaller voids in the shape to simulate muscles contracting and expanding. The ensuing robots, each and every about the size of a bar of soap, crept along like blocky minor cartoon figures.
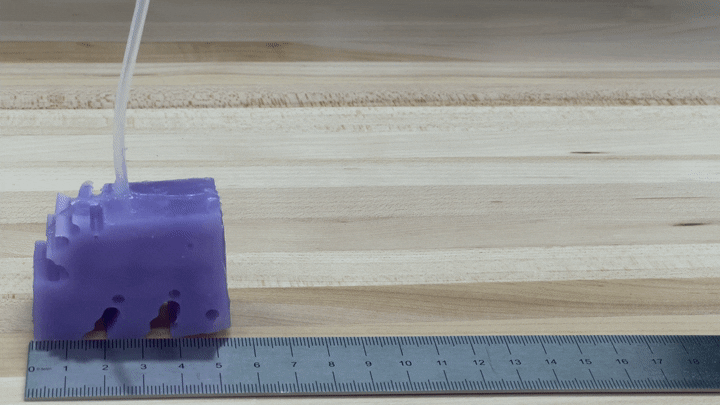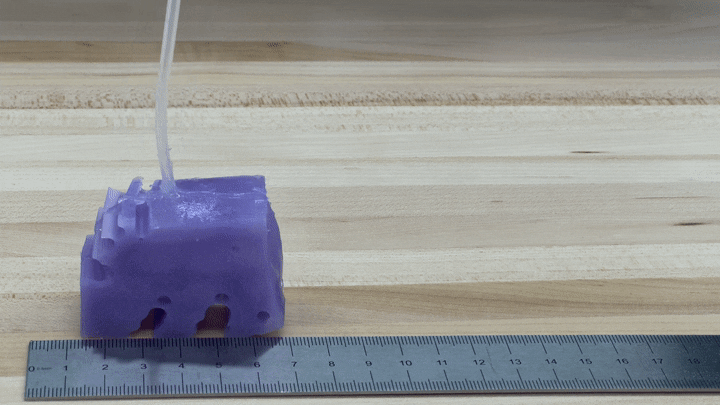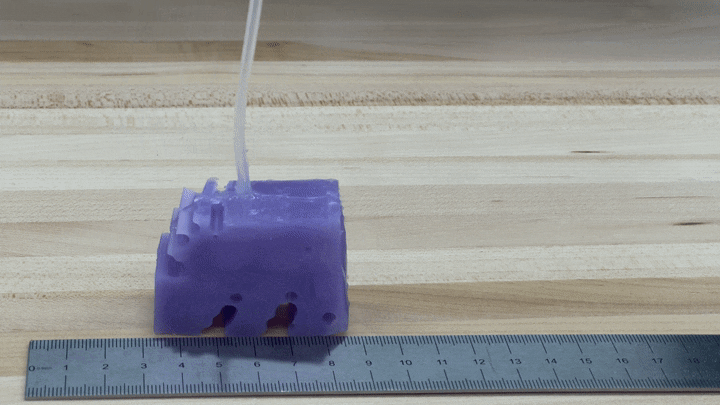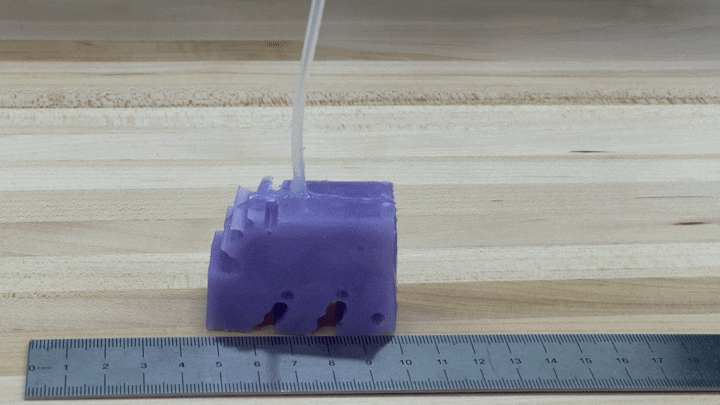 

“We’re seriously fired up about it just shifting in the ideal direction and moving at all,” Kriegman states, for the reason that AI-simulated robots never necessarily translate into the actual world.
The investigate signifies a move towards far more state-of-the-art robotic structure, even however the robots are pretty easy and can total only a single activity, suggests N. Katherine Hayles, a professor emerita at Duke University and a investigation professor at the College of California, Los Angeles. She is also writer of How We Turned Posthuman: Virtual Bodies in Cybernetics, Literature, and Informatics (College of Chicago Push, 1999). The gradient descent method is previously perfectly-proven in planning artificial neural networks, or neural nets—approaches to AI influenced by the human brain—so it would be potent to put brains and bodies with each other, she suggests.
“The serious breakthrough below, in my viewpoint, is heading to be when you just take the gradient descent procedures to evolve neural nets and join them up with an evolvable overall body,” Hayles says. The two can then coevolve, as transpires in dwelling organisms.
AI that can design and style new products could get humans unstuck from a wide range of pernicious issues, Lipson claims, from developing the future-era batteries that could support ameliorate local weather transform to acquiring new antibiotics and remedies for at present uncurable health conditions. These straightforward, chunky robots are a action toward this goal, he suggests.
“If we can design and style algorithms that can style items for us, all bets are off,” Lipson states. “We are likely to working experience an unbelievable enhance.”
[ad_2]
Resource website link






