[ad_1]
An increasing range of researchers is turning to synthetic intelligence (AI) to keep an eye on biodiversity and bolster endeavours to support endangered species. Unlike traditional techniques that can disrupt ecosystems or require appreciable time, labour and sources, AI has the possible to promptly and effectively analyse huge portions of true-earth details.
“Without AI, we’re hardly ever likely to reach the UN’s targets for safeguarding endangered species,” suggests Carl Chalmers, who studies machine mastering at Conservation AI, a Uk-based mostly non-profit firm in Liverpool that makes use of AI technological innovation for a variety of ecology jobs.
Species are vanishing at a charge hundreds to 1000’s of occasions more rapidly than that hundreds of thousands of several years ago, with up to 1 million species on the brink of extinction. In reaction, the United Nations set a purpose in 2020 to safeguard at minimum 30% of Earth’s land and oceans by the finish of the 10 years.
AI is “imperfect” but could speed up crucial discoveries, claims Nicolas Miailhe, Paris-centered founder of The Foreseeable future Culture, an intercontinental non-income firm that aims to far better govern AI. “We extremely substantially will need human practitioners in the loop to style types, as nicely as obtain, label, good quality check and interpret facts,” he claims.
Soundscape examination
Ecologist Jörg Müller at the University of Würzburg, Germany, and his colleagues have proven that AI tools can assistance to quantify biodiversity in tropical forests by pinpointing animal species from audio recordings.
In a research posted on 17 October in Character Communications, the scientists utilized AI to analyse animal ‘soundscapes’ in the Chocó, a region in Ecuador acknowledged for its abundant species diversity. They positioned recorders in 43 plots of land symbolizing distinct phases of restoration: forests that have been untouched by deforestation, regions that experienced been cleared but then deserted and had started off to regrow, and deforested land actively applied for cacao plantations and pasture. They gave the audio files to gurus, who were being able to discover 183 chook, 41 amphibian and 3 mammalian species.
The scientists also fed their recordings to a variety of AI model known as a convolutional neural network (CNN), which experienced previously been formulated to establish fowl appears. The CNN was in a position to select out 75 of the hen species that the specialists had, but the model’s information set was restricted and contained only 77 hen species that may manifest in the region. “Our effects show that AI is ready for additional comprehensive species identification in the tropics from audio,” suggests Müller. “All that is required now is a lot more training facts collected by individuals.”
The crew says that making use of AI to exactly measure the biodiversity of regenerated forests could be important for evaluating biodiversity tasks that ought to exhibit results to safe continued funding.
Digital camera-lure footage
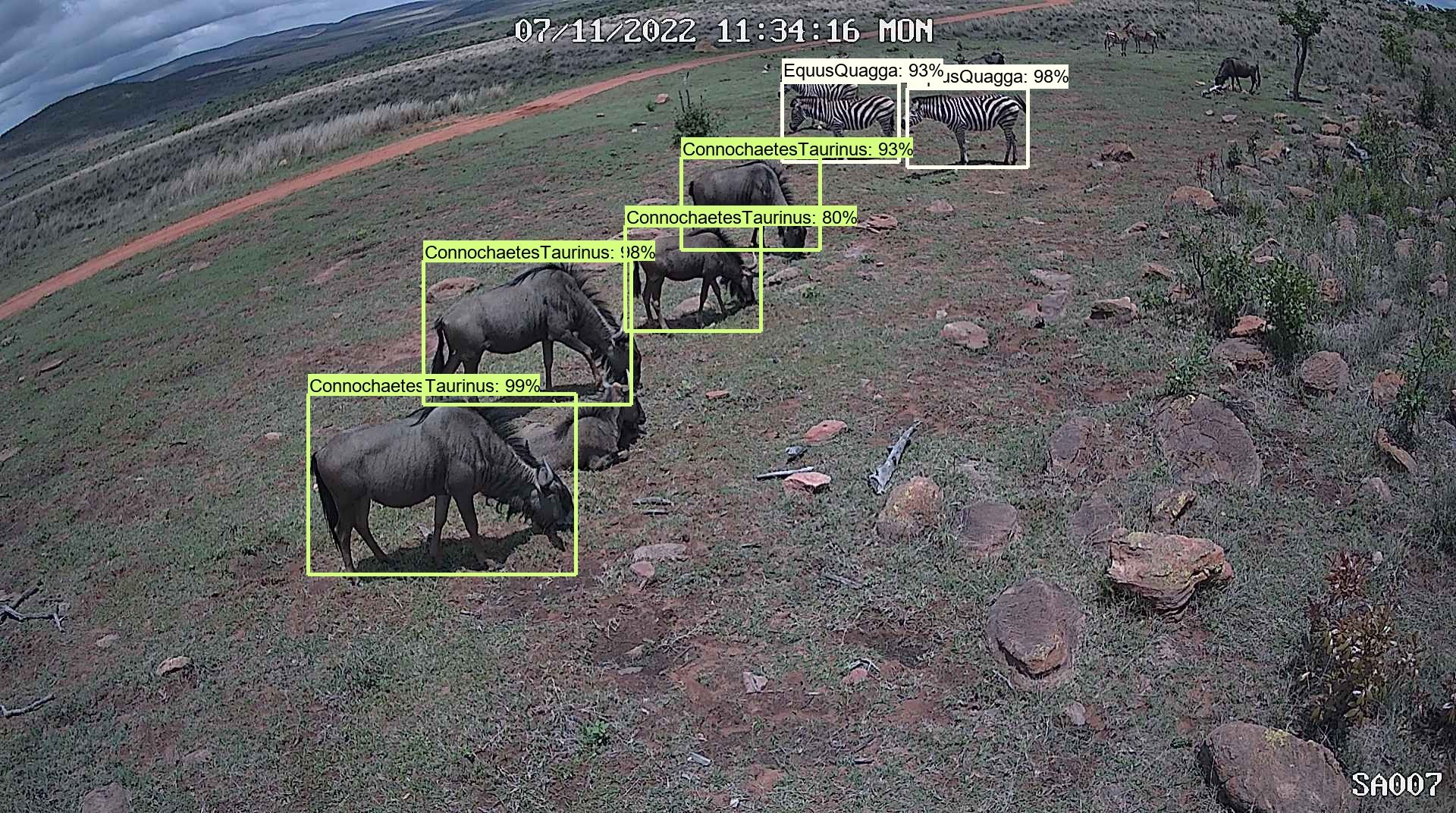
Scientists at Conservation AI have designed styles that can scour as a result of footage and visuals from drones or camera traps to identify wildlife — which includes critically endangered species — and observe animal actions.
They developed a no cost on the internet system that takes advantage of the technological innovation to quickly analyse photos, video or audio information, together with details from actual-time digital camera-lure footage and other sensors that approved people can upload. Buyers have the possibility to be notified by e-mail when a species of fascination has been spotted in the footage they have uploaded.
So considerably, Conservation AI has processed a lot more than 12.5 million visuals and detected a lot more than 4 million personal animal appearances across 68 species, like endangered pangolins in Uganda, gorillas in Gabon and orangutans in Malaysia. “The system can course of action tens of thousands of images an hour, in contrast to human beings who can do a handful of thousand at very best,” suggests Paul Fergus, 1 of Conservation AI’s lead researchers. “The pace at which AI procedures knowledge could make it possible for conservationists to shield susceptible species from unexpected threats — such as poaching and fires — speedily,” he provides. Conservation AI has currently caught a pangolin poacher in the act by analysing footage in actual time.

As perfectly as checking biodiversity in actual time, AI can be used to model the impacts of human actions on an ecosystem and reconstruct historical changes. Scientists have employed AI to uncover how a century’s really worth of environmental degradation in a freshwater ecosystem has led to biodiversity loss.
Although it is perfectly documented that human activities have resulted in biodiversity decline in rivers and lakes, little is regarded about which environmental factors have the biggest impact. “Long-phrase information is pivotal to connection alterations in biodiversity to environmental adjust and to determine achievable conservation objectives,” says Luisa Orsini, who studies evolutionary biosystems at the College of Birmingham, Uk.
Orsini and her colleagues formulated a design that inbound links biodiversity to historic environmental improvements applying AI. In a study released in eLife earlier this calendar year, the workforce attained genetic material that had been remaining driving around the past century by vegetation, animals and bacteria in the sediment of a lake. The sediment layers had been dated and environmental DNA was extracted for sequencing.
The experts then merged these facts with climate info from a weather station and chemical-pollution facts from direct measurements and countrywide surveys, applying an AI developed to cope with assorted kinds of info. Orsini claims the intention was to discover correlations among the the ‘mayhem’ of knowledge.
They identified that the presence of pesticides and fungicides, alongside one another with extreme-temperature activities and precipitation, could reveal up to 90% of the biodiversity decline in the lake. “Learning from the past, we showcased the price of AI-centered techniques for knowledge previous motorists of biodiversity loss,” says examine co-creator Jiarui Zhou, who is also at the College of Birmingham.
The key advantage of employing AI is that it is speculation cost-free and details driven, says Orsini. “AI ‘learns’ from past information and predicts potential traits in biodiversity with better accuracy than ever accomplished just before.”
Miailhe is hopeful that AI can be routinely applied to actual-earth conservation attempts in the in the vicinity of future. “That’s clearly the way to go,” he suggests. But he warns that AI consumes computing electrical power and substance resources, which finally has adverse outcomes on ecosystems. “Environmental effects assessments need to be at the centre of AI possibility administration,” he claims.
This report is reproduced with authorization and was first published on October 27, 2023.
[ad_2]
Supply website link






