[ad_1]
Is the solar an only little one? Or was it born into a (quite, very) significant spouse and children?
The reply tells us more than just how uncomfortable getaway loved ones reunions can be (if you feel yours are lousy, imagine how significantly even worse it would be with a couple thousand sibling rivals). Right after all, the sun’s origin tale is, in the end, our possess. We’ve witnessed big leaps in our comprehension of how stars kind, but, ironically, we still have some rather fundamental inquiries left about our closest, dearest one particular. This kind of as, regardless of whether the sunshine was born solo or along with a massive passel of other stars.
Regardless of the solar remaining shut ample that we can nearly touch it, the greatest dilemma with finding its origin story is that it’s outdated. Born 4.6 billion many years back, our star is nicely into center age and has wandered considerably from its ancestral home—some nameless, now-vanished “stellar nursery” of gasoline that very long back dispersed or consolidated into stars.
We just cannot locate that nursery, but we can continue to master about it. We have some evidence of it, perhaps shockingly, in the form of meteorites, some of which nevertheless have clues about the gestational atmosphere all around them through the birth of the photo voltaic technique. For instance, isotopes of factors like potassium inside of meteorites have informed us wherever in the presolar nebula they formed, and versions involving meteorites can be applied to support establish the nebula’s situations very well just before the emergence of any planets.
With information from meteorites in hand and aided by condition-of-the-art laptop simulations, an international crew of astronomers investigated the probable natal atmosphere of the sunlight and lately released its effects in the Regular monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Culture. Employing a intelligent line of reasoning, their analysis suggests the sunshine not only experienced several siblings but spawned in rather a metropolitan community.
Stars are born in cosmic clouds called nebulae, forming when their interiors collapse onto a central pilelike point that gets the nascent star. Nebulae appear in quite a few shapes and dimensions, from modest dark globules to enormous big molecular clouds. How a star sorts in any offered nebula is a lot extra a tale of character than of nurture.

For example, the nearby nebula Barnard 68 is a darkish clot of chilly gasoline and dust—tiny grains of silicates (rocky product) and intricate carbon molecules very similar to soot—relatively near to us in room, only a handful of hundred gentle-decades away. It’s a single of my beloved objects an eerie, pitch-black ghostly mass that utterly blocks all light from stars at the rear of it, like an opaque hole in the sky.
It’s only 50 percent a light-weight-yr across (just about a few trillion miles), with hardly plenty of substance in it to make a one star a little bit heftier than the sun. It is very likely in the center of that system now, and could transmogrify alone into a star in as little as 200,000 decades.
On the other end of the scale, we have the Orion B molecular cloud intricate, a certainly tremendous web page of active star formation which is more than a thousand gentle-a long time absent and numerous hundreds of light-weight-yrs across. It is beefy ample to make a staggering number of stars—at minimum 100,000 like the sun. The iconic Orion nebula, seen to the bare eye and the birthplace of hundreds of stars, is only one particular modest part of this enormous stellar factory.
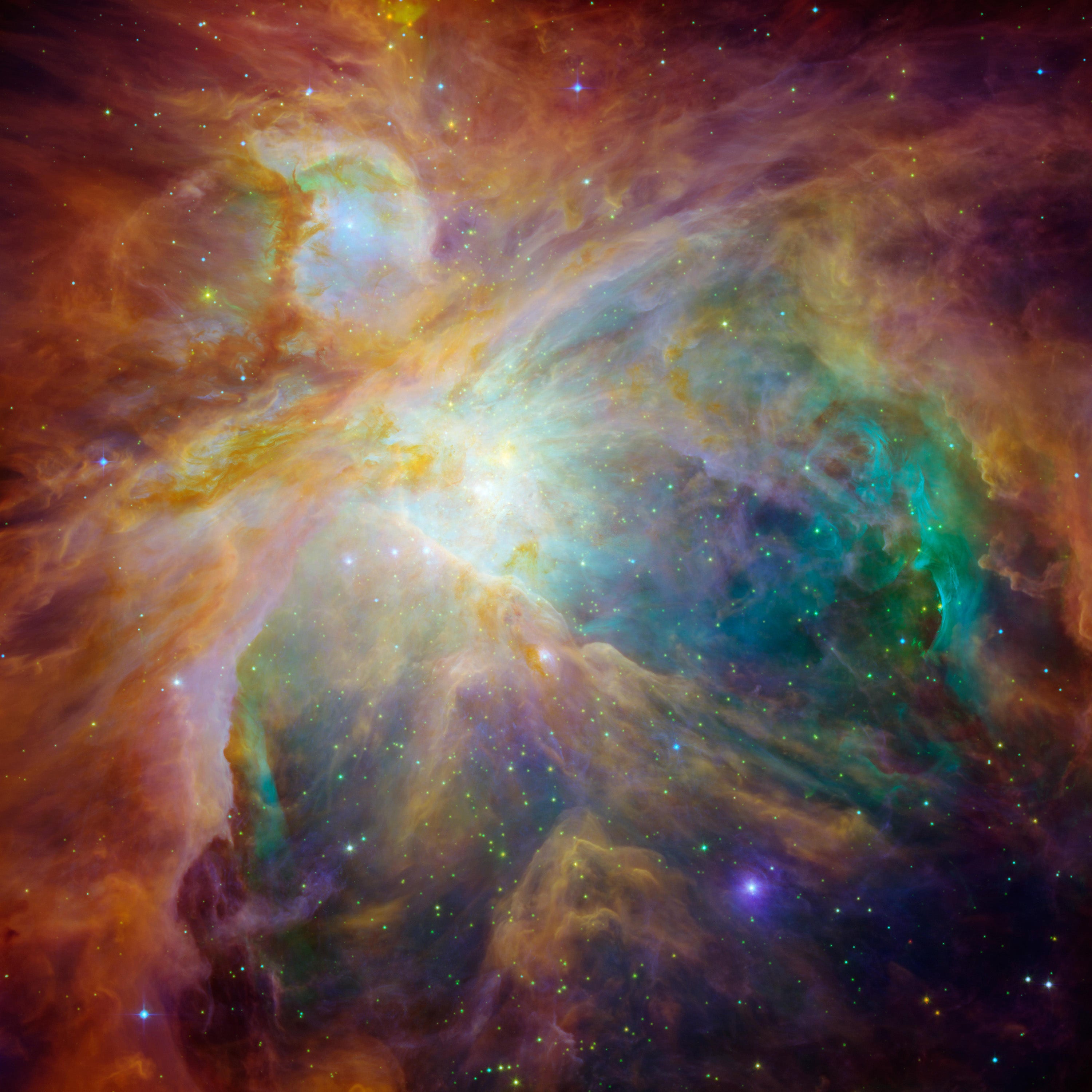
 

Large clouds like this are relatively exceptional but crank out stars on an industrial scale, whilst the more compact clouds are a lot less fecund but litter the galaxy. Just on the lookout at those figures statistically it is not possible to discern the origin of the solar: it could have arrive from both kind of stellar nursery.
On the other hand, these nebular environments are vastly unique, which has an effect on the stars they make. Large stars observed in a nebula have a huge impact on their gestating siblings. They can blast out intense winds of subatomic particles—like the solar wind but ramped up way earlier 11. These winds can seed forming stars with weighty aspects like aluminum and magnesium. And later on, when they explode as supernovae, they fling a various mix of these things, this kind of as iron and cobalt, a really very long way.
Massive stars, however, are unusual. It’s possible a person out of a hundred stars is enormous plenty of to keep this form of sway, and modest nebulae merely do not make them. That usually means, in principle, hunting at the chemical composition of the early photo voltaic program could explain to us in what type of nursery the sun was born.
This was the aim of the newly revealed study. The astronomers looked at two elements in unique: aluminum-26 and iron-60. Aluminum-26 is developed inside massive stars and blown out in their winds, though iron-60 is cast in the thermonuclear hell of an exploding star. Equally aspects are radioactive, decaying into magnesium and cobalt, so thoroughly measuring the amounts of these daughter elements in pristine samples from the earliest times of the photo voltaic system—from meteorites, that is—can explain to us about the ecosystem in which the solar shaped.
For their new analysis, the worldwide group of researchers made use of the physics of nebulae and star development to simulate a sunlike star’s start in a selection of environments, from nebulae that contains really couple of stars (a proxy for more compact clouds) up to massive kinds with numerous hundreds. Future, they calculated the elemental composition of the proto-proxy-presolar disk that emerged in every single a person, then compared these virtual yields against what’s essentially measured in meteorites.
Their outcomes show that as it formed in its natal disk, the early solar was probable pummeled by powerful winds and supernovae explosions—both sourced from large stars. That usually means the photo voltaic nursery was more like the Orion complicated than Barnard 68.
In other words, the sun was in all probability a lot more of a downtown city child than a rural tiny-town star. Of system, with its nebular nursery gone, we can’t ensure this very easily. Immediately after all, you just cannot go house once again.
And what of the sun’s siblings, the hundreds of other stars in its extended loved ones? Like the sunshine, they at the time nestled collectively like a litter of puppies, but possible wandered out on their own eons ago, and are now orphaned, scattered across the galaxy. Even now, astronomers do appear for them—ones with the very same age and composition as the sun—so that we can learn far more about our parent star.
A reunion is quite unlikely. If we want to see a relatives album, we’ll just have to set it jointly ourselves.
This is an opinion and analysis write-up, and the sights expressed by the writer or authors are not essentially these of Scientific American.
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink






